外文翻译-被动阻尼器对道路车辆保险杠衰减效果的实验评价.doc
三轴五档变速器的设计与校核【含CAD图纸、说明书】
收藏
资源目录

压缩包内文档预览:
编号:22909156
类型:共享资源
大小:1.88MB
格式:ZIP
上传时间:2019-11-04
上传人:机****料
认证信息
个人认证
高**(实名认证)
河南
IP属地:河南
50
积分
- 关 键 词:
-
含CAD图纸、说明书
五档
变速器
设计
校核
CAD
图纸
说明书
- 资源描述:
-
【温馨提示】压缩包内含CAD图有下方大图片预览,下拉即可直观呈现眼前查看、尽收眼底纵观。打包内容里dwg后缀的文件为CAD图,可编辑,无水印,高清图,压缩包内文档可直接点开预览,需要原稿请自助充值下载,所见才能所得,请见压缩包内的文件及下方预览,请细心查看有疑问可以咨询QQ:11970985或197216396
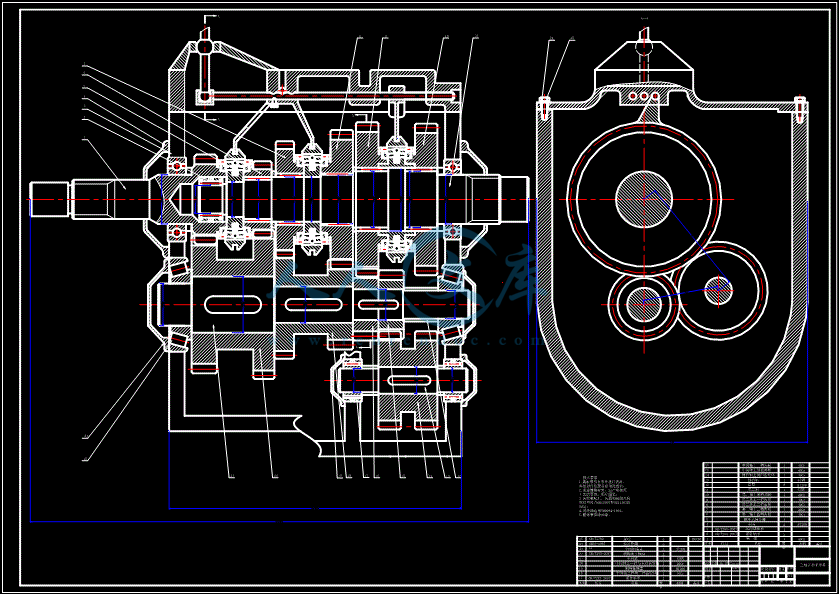

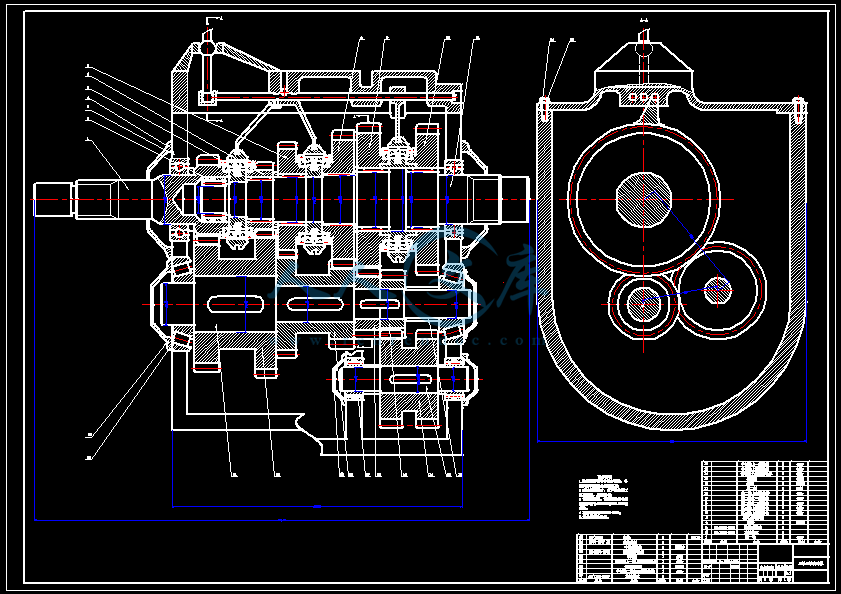
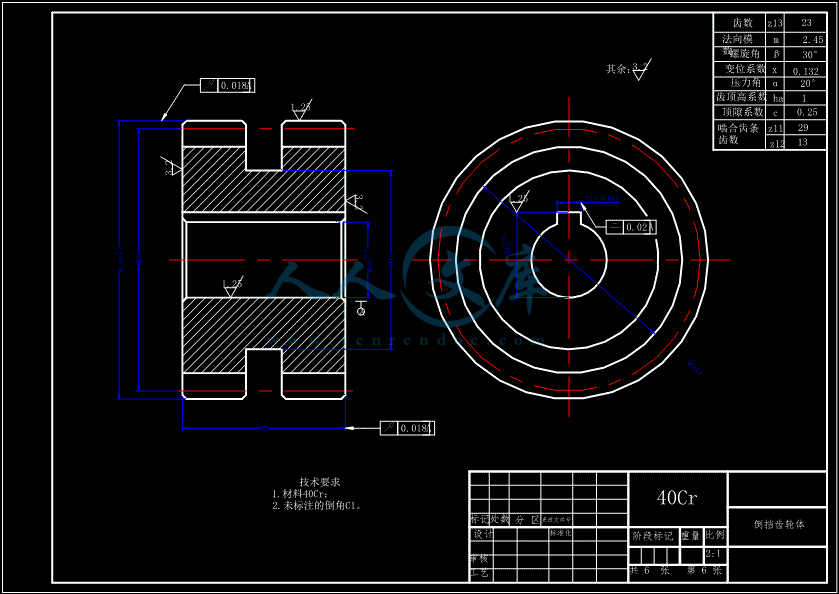
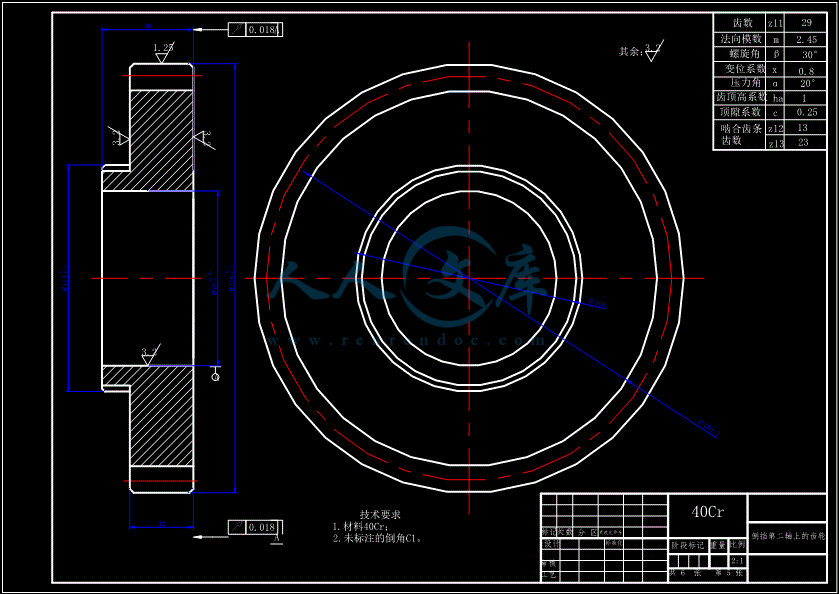


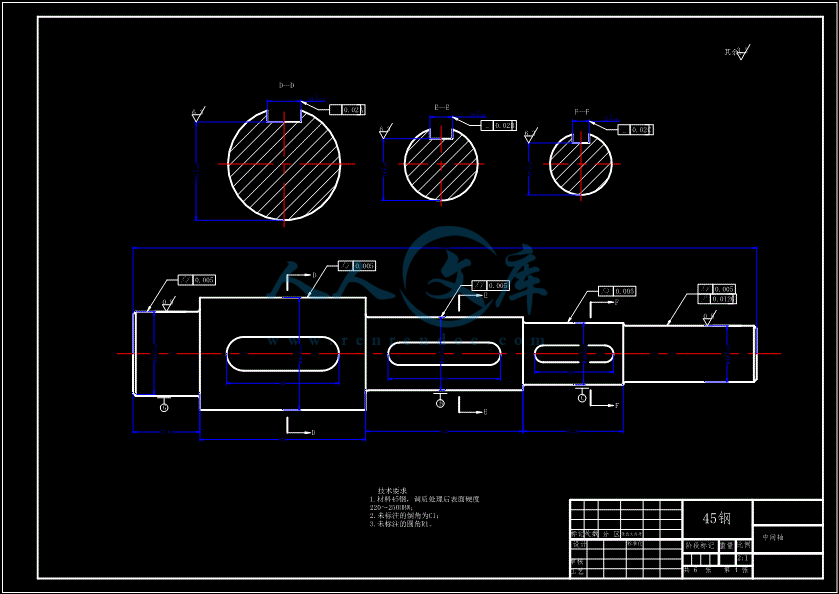



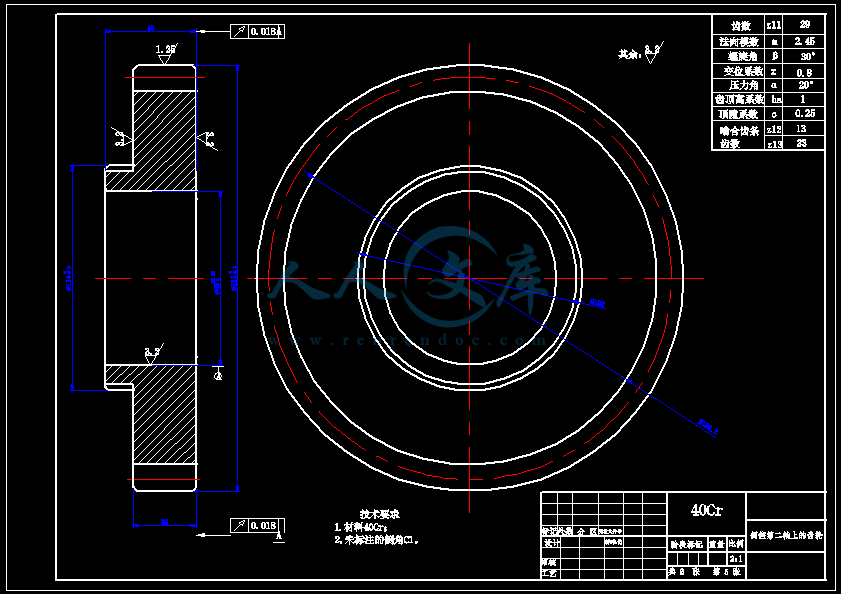
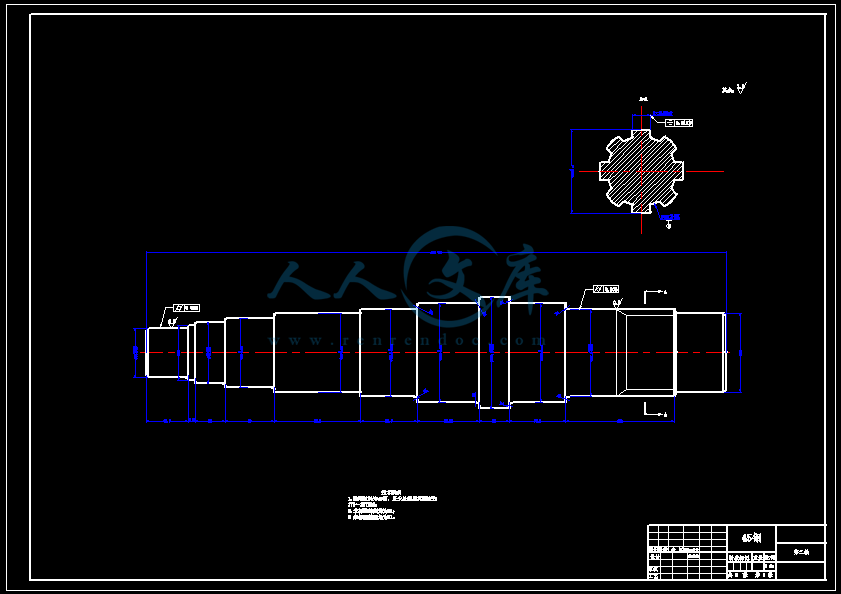
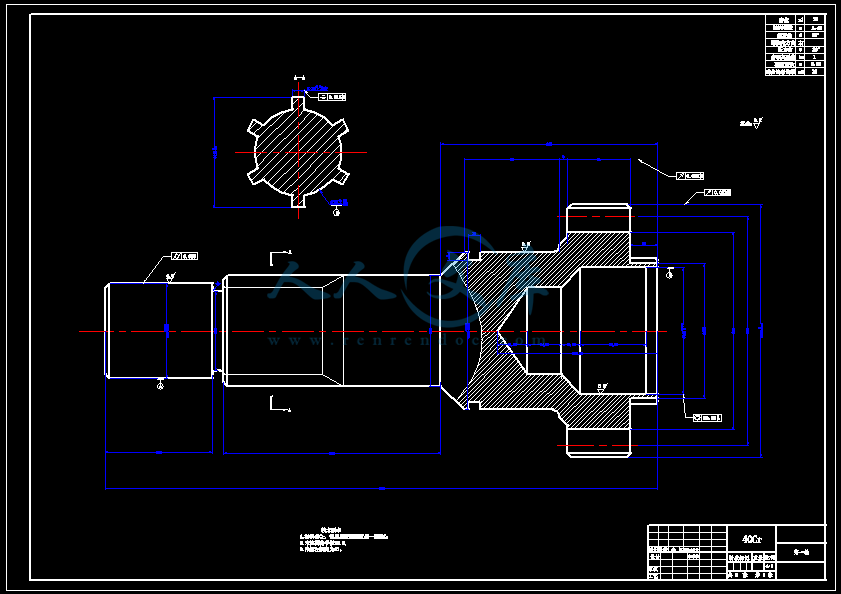







- 内容简介:
-
毕 业 设 计(论 文)外 文 参 考 资 料 及 译 文译文题目: Experimental Evaluation of the Attenuation Effect of a Passive Damper on a Road Vehicle Bumper 被动阻尼器对道路车辆保险杠 衰减效果的实验评价 学生姓名: 学 号: 专 业: 所在学院: 指导教师: 职 称: 20xx年 2月 27日说明:要求学生结合毕业设计(论文)课题参阅一篇以上的外文资料,并翻译至少一万印刷符(或译出3千汉字)以上的译文。译文原则上要求打印(如手写,一律用400字方格稿纸书写),连同学校提供的统一封面及英文原文装订,于毕业设计(论文)工作开始后2周内完成,作为成绩考核的一部分。外文原文Experimental Evaluation of the Attenuation Effect of a Passive Damper on a Road Vehicle BumperAbstract:To mitigate the degree of damage to passengers caused by automobile collisions, a friction damper was built and used in experimental tests to test its effectiveness in impact energy attenuation. The study revealed that energy absorption capacity of a bumper can be improved with the addition of a friction damper. The results revealed that the addition of the friction damper to an automobile bumper to give a bumper-damper system could attenuate about 32.5 % more energy than with the bumper alone. It can be concluded that the effectiveness of automobile bumpers to withstand impact of vehicles by absorbing the kinetic energy from the impact can be improved with the use of a passive friction damper. That is, a passive friction damper system could be used to attenuate more road vehicle impact energy in collisions.Keywords:Vehicle Bumper, Equivalent Energy Speed (EES), Impact Attenuation, Passive Damper1. IntroductionOver the past 20 to 30 years, Bumper design concepts have changed drastically. EEA 6 describes four basic bumper design principles (Where necessary, specific features can also be combined). They are: First, the traditional design with a visible metallic transverse beam that decorates the front or rear end of the vehicle and acts as the primary energy absorber during collision; which is seldom used today. Secondly, the plastic fascia and reinforcing beam system that is fixed directly to the front/rear longitudinal beams. This design increases the overall vehicle crashworthiness but leads to a small sacrifice in bumper performance. Thirdly, the system consisting of three components: a plastic fascia, a reinforcing beam and mechanical energy absorbers. The energy absorbers come in two types. They may be either of a reversible type (“shock absorbers”) or deformation elements (“crash boxes”) which are usually replaced after a crash. Lastly, a system, which is more pedestrian friendly in leg impact, which includes a plastic fascia, a reinforcing beam and a propylene foam or a honeycomb energy absorber placed between the plastic fascias and reinforcing beam.An automobile bumper is the front-most or rear-most part, specially designed to allow the car to sustain low speed impact without damage to the vehicles safety systems. That is, they are not capable of reducing injury to vehicle occupants in high speed impacts 7 8. It is required to pass an impact test at 4 km/h (2.5 mph) with novisible damage to the body. Bumpers keep safety-related equipment such as headlights and taillights, hoods, fenders, exhaust and cooling systems, away from damage. Some bumper designs have the provision of cushioning and support of the lower limb; as well as the integration of impact sensors and exterior airbags 9. The main method proposed for cushioning the lower limb in an impact uses an energy absorber in front of a semi-rigid beam. Energy absorbers proposed include plastic foams (single or multi-density), molded plastic “egg-crates”,“spring-steel”, composite steel-foam, and crush-can energy absorbers 9. Exposed steel bumpers that involvefrontal airbags design are also alternative design concepts that appear to be adaptable to meet the pedestrians safety requirements but these may be costly and require advanced sensors to function efficiently 9.Bumpers could be designed to absorb more energy than they usually do with some modification of the design and possibly with the use of additional energy absorption devices. This work seeks to apply a passive control system which is an uncontrolled damper that requires no input power to operate. Passive control systems attenuate or absorb vibrations automatically without the need of an electrical control system. They are simple and generally low in cost, but are unable to adapt to changing needs after installation. The passive control system was selected for this work because of its stability, simplicity and low cost in its application. Passive systems include base isolation systems, viscoelastic dampers, bracing systems and friction dampers 12. Base isolation systems are used to isolate the dynamic force transfer from the structure to the base. Viscoelastic dampers attenuate the force due to external loads using their natural damping properties. Bracing systems are usually made up of brace frames and are usually used to permanently stabilize buildings from external forces such as wind loads and earthquakes by stiffening the structural components; and lastly friction elements consist of dampers that use dry friction to dissipate energy. They are also referred to as Coulomb Damping Systems. Wittman 13 suggested the use of friction to absorb kinetic energy in crash situations by regulating the amount of pressure or normal force on the friction element. The friction element was selected for this study because it does not need external energy, it is robust, and low cost. Even though viscous damping shares most of these advantages, the friction dampers dryness and therefore no risk of leakages during operation makes it preferable. Although using friction to absorb energy has a big potential, little has been done to exploit it in attenuating crash energy.Figure 1 shows that, males of age 15 to 44 years are more likely to be involved in road traffic crashes than females. Most breadwinners of families and communities are males in the developing world. Since about 90% of all traffic deaths occur in the developing world, and the majority of these victims are in their most productive years, road crashes are taking a big toll on the livelihood at majority of people on earth 3. This is a cause for concern that needs to be addressed.King et al. 14 reported that bumper systems on passenger cars available in North America, though built to meet specific government standards, had different impact characteristics among different vehicles and that certain vehicles could sustain significant front or rear impacts without sustaining damage. There have been efforts to improve on the energy absorption capacity of the bumper. For example, bumper isolators are shock absorbers that are mounted between the vehicle frame and bumper, and are specially designed to reduce an amount of property damage to vehicles 15. Impact attenuation has been investigated by different people using different methods over several years. Grassie 16 17 investigated the dynamic load attenuation by rail pads in laboratory and on track. Esveld 18 claims that ballasted railway track had many superior advantages.By using stiffness of a vehicle and its components, the kinetic energy loss in deformation on vehicles can be estimated. In an investigation, Vangi 19 estimated the stiffness of a vehicle by estimating the geometric parameters of the damage starting from a photograph of generic damage, with documented Equivalent Energy Speed (EES), on a vehicle of the same model as the one under investigation. This method was validated performing crash tests and using data from crash tests found in the literature. The method estimated the kinetic energy loss in deformation on vehicles with sufficient accuracy 19.Different impact attenuation measures have been used in the railway industry, for example, to mitigate the effect of high forces on the sleeper. In one of such examples, the force content is filtered and attenuated by the softening medium, rail pad installed between sleeper and rail 20. Similar measures can be introduced in the automobile bumper system to improve its mitigation of high impact forces at higher speeds. Kaewunruen and Remennikov 21, in their test to find the effect of impact loads on railway seats, used a drop hammer and a specially designed fixture to transfer the impact load to the specimens. This study aims at helping to solve part of this serious problem through the development of a more effective crash attenuation system. Hence, the objective of this work is to find out experimentally, whether the addition of a passive damper to a road vehicle bumper could improve its impact energy absorption capability.Figure 1. Global road traffic fatalities by sex and age (Source: 3).2. Material and MethodAn experiment was performed using an impact test machine to investigate whether the impact attenuation capacity of a bumper could be enhanced with the addition of a friction damper. A model of friction damper was designed using springs with a definite stiffness. Special fixtures were made to adapt the impact test machine to the test conditions. Fixtures were fastened to the hammer and machine to give a good surface for the impact. The impact fixture was made in the shape of an L, with webs to strengthen the welded joints. This was clamped to the impact machine as shown in the schematic diagram in Figure 2.During the experiment, the bumper specimen and the bumper-damper combination, where applicable, were arranged together and the hammer of the impact machine allowed swinging freely to impact on it. The hammer of the impact test machine was raised to specific heights and allowed to fall under gravity to hit the bumper specimen in the experimental setup. During the experiments four different heights were used to give four impact forces.The angle at which the hammer swings from rest and the angle at which it impacts the test specimen were measured and noted. The angle is as indicated in the schematic diagram in Figure 3. The deformation on the bumper specimen after the impact was measured with a veneer caliper and noted. Figure 2. Impact test machine with impact (R) and hammer (O) fixtures. Figure 3. Schematic of a simplified pendulum hammer of an impact test machine.Destructive impact tests were performed on pieces of the bumper specimen. Specimen from two bumpers B and C, from two different cars were used in the analysis. 4 specimens of bumper B and 8 specimens of bumper C were used. The average length of the specimen was 35 cm. The specimen, and where applicable both specimen and damper, were put together, placed on the impact fixture and the hammer allowed to swing freely to impact on it/them.The friction damper was made with springs of stiffness 44 kN/m. For bumper B, the four bumpers were tested without a friction damper; but for bumper C, four specimens were tested without a damper, and four tested with a damper. The impact forces during the tests were computed and used in the analysis. The results obtained for the two sets of tests are tabulated and presented in Table 1. Bumper B, tested without a damper, was to help establish whether bumper C without a friction element will follow a similar trend. It can be observed that for both bumper samples, results increase steadily with increase in impact load in a linear way. However, the deformation in bumper C is much higher than that of bumper B for the same impact forces. This may be due to the different material properties in the different bumpers. When a friction element was added, in the case of bumper C,the same forces as used in the previous tests, where no friction element was added, could not be used. The now shorter distance of travel of the pendulum to impact on the Bumper-Damper arrangement would not allow the same impact forces to be used. The results show that with increase in impact forces, the deformation starts increasing very slightly at first but at the higher impact force of 9078.95 N it increases drastically from 9 mm (for 7438.27 N) to 27 mm, showing an exponential trend. Curve-fitting method was used to present the curves of the experimental results as described in the next section.3. ConclusionA friction damper was built and tested with a bumper to check for its effectiveness to attenuate impact energy. The study showed that energy absorption capacity of a bumper can be improved with the addition of a friction damper. The experimental results revealed that the addition of the friction damper to a bumper to give a bumper damper system could attenuate about 32.5% more energy than with the bumper alone. It can be concluded that the effectiveness of automobile bumpers to withstand impact of vehicles by absorbing the kinetic energy from the impact can be improved with the use of a friction damper.中文译文被动阻尼器对道路车辆保险杠衰减效果的实验评价摘要:为了减轻汽车因碰撞引起乘客的伤害程度,从而建立和使用摩擦阻尼器,并进行了实验测试,以验证其有效性的能量衰减。这项研究表明,增加保险杠的能量吸收能力,可以提高摩擦阻尼器。结果表明,添加了摩擦阻尼器的汽车保险杠比没有添加摩擦阻尼器的保险杠衰减约32.5%以上的能量。可以得出结论,汽车保险杠有效抵御车辆的动能,摩擦阻尼器从冲击中吸取动能。也就是说,一个被动摩擦阻尼器系统可以用来衰减更多道路车辆碰撞能量。关键词:汽车保险杠、能量等效速度(EES),影响衰减,被动阻尼器1介绍在过去的20到30年里,保险杠的设计理念发生了巨大的变化。EEA 6描述了四种基本的保险杠设计原则(在必要的时候,具体的功能也可以结合)。它们是:首先,传统的设计是把车辆的前方或后方的可见金属横梁装饰和车辆碰撞期间作为主要的能量吸收器;这重如今已经很少使用了。其次,用塑料筋膜和加强梁直接固定前/后纵向梁。这样的设计增加了汽车的整体碰撞性能而保险杠性能则有所衰减的。第三,系统的控制由三部分组成:一个塑料筋膜,加强梁和机械能量吸收器。能量吸收器有两种类型,他们一个是可逆式(“减震器”)另一个是变形的因素(“碰撞盒”)碰撞盒通常是崩溃后更换的。最后一个系统,是对行人腿部冲击的一个保护,其中包括一个塑料筋膜,一个加强梁和一个丙烯泡沫或塑料面板和加强梁之间放置的蜂窝能量吸收器。汽车保险杠是装在汽车的前后端,用来吸收和缓冲外界冲击力的汽车安全系统。也就是说,他们能够减少车辆在高速碰撞时的影响7 8。这是需要通过一个冲击试验来证明,在4公里/小时(2.5英里),身体没有可见的损害。保险杠保持安全的相关设备如前大灯和尾灯罩,挡泥板、排气和冷却系统。一些保险杠的设计提供了对缓冲垫的支持,以及传感器的影响和外部安全气囊的集成9。主要建议用前端的半刚性梁来缓冲下肢的冲击。能量吸收器包括塑料泡沫(单个或多个密度),模压塑料蛋箱,“弹簧钢”,复合钢泡沫,破碎能吸能器9。暴露的钢保险杠,包括正面安全气囊的设计以及不同的设计概念的出现都是为了适应和满足行人的安全要求,但这可能是昂贵的,需要先进的传感器来发挥有效的功能9。保险杠的设计可以吸收比他们通常做一些修改的设计更多的能量并可能使用额外的能量吸收装置。这项工作旨在应用被动控制系统是一种不受控制的阻尼器,不需要输入功率来操作。被动控制系统对没有电气控制系统的需要减弱或吸收振动自动。他们很简单一般成本较低,但安装后无法适应变化的需要。被动控制系统由于其稳定性、简单性和低成本的应用而被选为这项工作。被动系统包括基础隔震系统,粘弹性阻尼器,支撑系统和摩擦阻尼器12。基础隔震系统是用来隔离从结构的动态力的基础。粘弹性阻尼器衰减由于采用自然阻尼性能的外部荷载力。支撑系统通常是由支撑框架,通常用于从外部力量,如风的永久稳定建筑物荷载和地震作用下的结构构件,最后的摩擦元件组成的阻尼器利用干摩擦耗散能量。他们也被称为库仑阻尼系统。威特曼13建议使用摩擦吸收动能在碰撞的情况下,通过调节压力的量或摩擦元件的法向力。本研究选择的摩擦元件,因为它不需要外部能源,它是强大的,低成本。即使粘滞阻尼股份的这些优势,在操作过程中,摩擦阻尼器的干燥,因此无泄漏使它更好。虽然使用摩擦吸收能量有巨大潜力,几乎没有衰减的碰撞能量利用。图1显示,年龄在15岁至44岁的男性更容易被卷入道路交通事故而不是女性。家庭最挣钱的人和社区发展中世界的男性。由于90%的交通死亡发生在发展中国家,大多数的这些受害者是在他们最具生产力的年,道路交通事故是在大多数人在地球上的生活造成了巨大的损失3。这是一个值得关注的原因,需要解决。King et al. 14报道说,在北美国的客运车辆保险杠系统,虽然建立以满足特定的政府标准,有不同的影响,在不同的车辆和某些车辆可能会保持显著正面或后方的影响,而不受损害。有努力提高保险杠的能量吸收能力。例如,保险杠减振器减震器安装到车架和保险杠之间
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 人人文库网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。

人人文库网所有资源均是用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流,未经上传用户书面授权,请勿作他用。
|
2:不支持迅雷下载,请使用浏览器下载
3:不支持QQ浏览器下载,请用其他浏览器
4:下载后的文档和图纸-无水印
5:文档经过压缩,下载后原文更清晰
|
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号